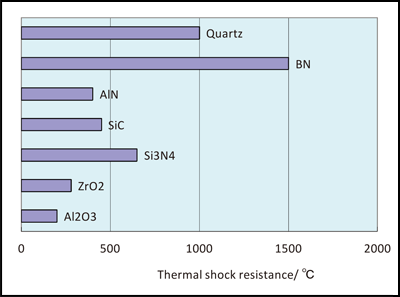
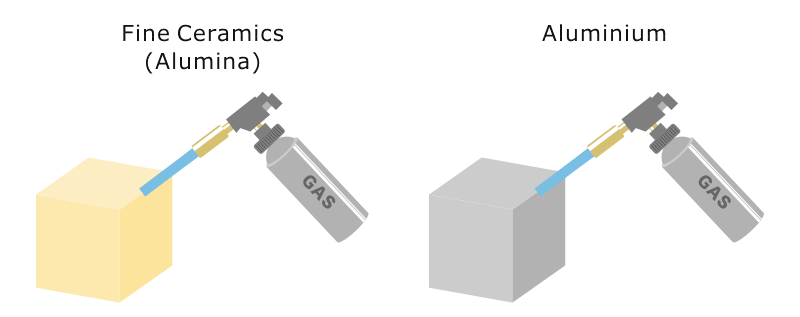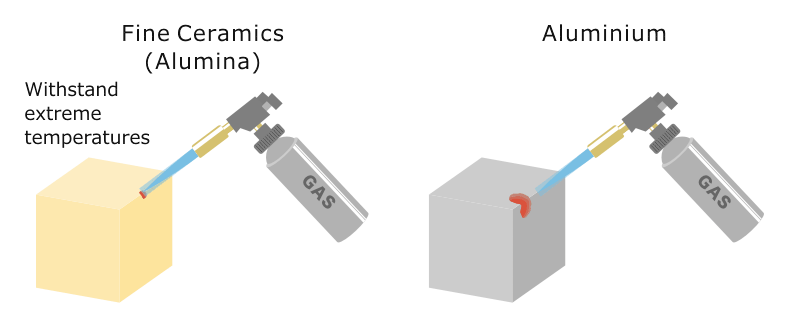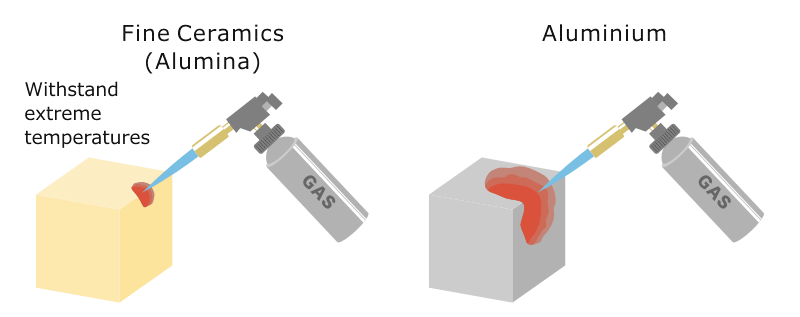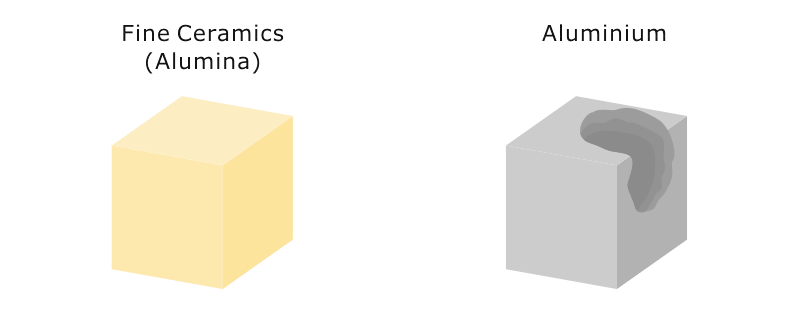
This paper focuses on heat loss estimation from a tes system operating at 800 insulated in a cylindrical ceramic crucible and the determination of the optimal insulation thickness of the.
Ceramic specific hear.
Specific heat capacity is amount of heat required to raise temperature of unit mass of material by one unit.
While the data in these charts is in most cases typical of what you will find from ceramic component suppliers it is only intended to be a general point of reference and should not be used for material selection or specification.
M material mass.
δt temperature rise.
This heat calculator or calorimetry calculator can help us determine the heat capacity of a sample that s heated or cooled.
C δq mδt where c specific heat capacity.
The specific heat of some commonly used solids is given in the table below.
Cordierite is a crystalline magnesium aluminosilicate.
Of al 13 ºfˉ 23 ºcˉ.
Heat capacity is amount of heat required to raise material temperature by one unit.
Specific heat capacity of ceramic materials is higher than that of metals.
Specific heat capacity.
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating selected and refined materials often including clay in the form of kaolinite to high temperatures.
Thermodynamics effects of work heat and energy on systems.
If we use the metric system the specific heat is the amount of heat that s needed for a sample which weighs 1 kg to elevate its temperature by 1k.
Ceramic matrix composites prepregs for parts requiring thermal performance up to 2200 f.
Of sic 2 3 ºfˉ 4 0 ºcˉ.
Air specific heat at constant temperature and varying pressure figures and table showing isobaric cp and isochoric cv specific heat of air at constant temperature and.
δq amount of heat.
The effect of crystallization on the lattice vibrations of two glass ceramics a magnesium aluminosilicate corning code 9606 and a lithium aluminosilicate corning code 9623 is studied through measurements of the thermal conductivity and specific heat below 300 k.
Thermal expansion of ceramic materials is generally lower than that of metals.
See also tabulated values of specific heat of gases food and foodstuff metals and semimetals common liquids and fluids and other common substances as well as values of molar heat capacity of common organic substances and inorganic substances.
Material properties material properties for gases fluids and solids densities specific heats viscosities and more.
For conversion of units use the specific heat online unit converter.