The zone where a material will return to its original shape for a given amount of stress toe region applies to a ligaments stress strain curve.
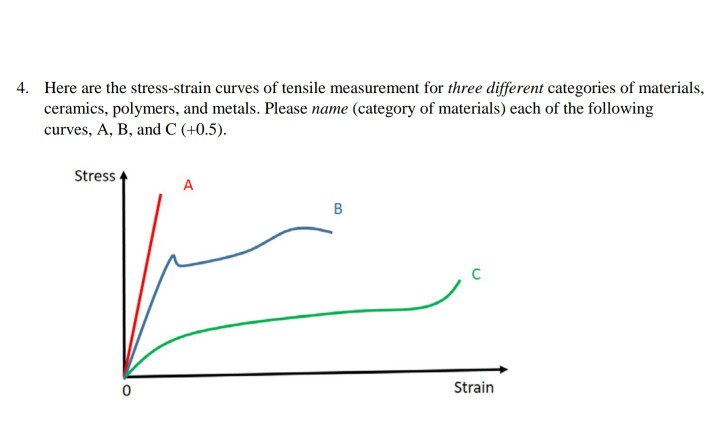
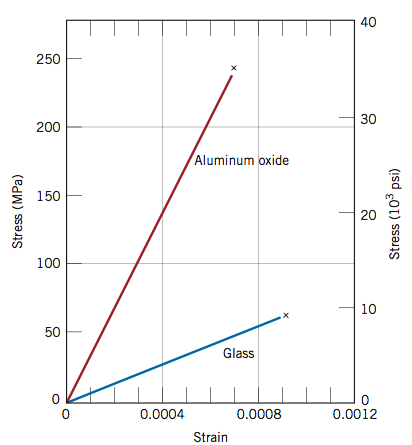
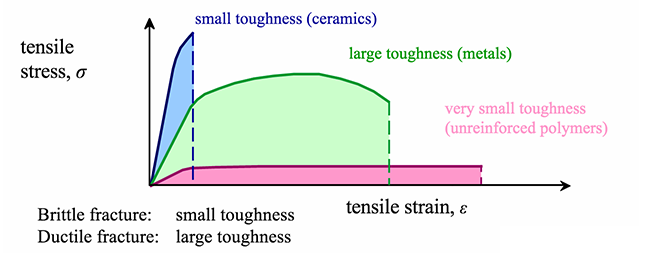
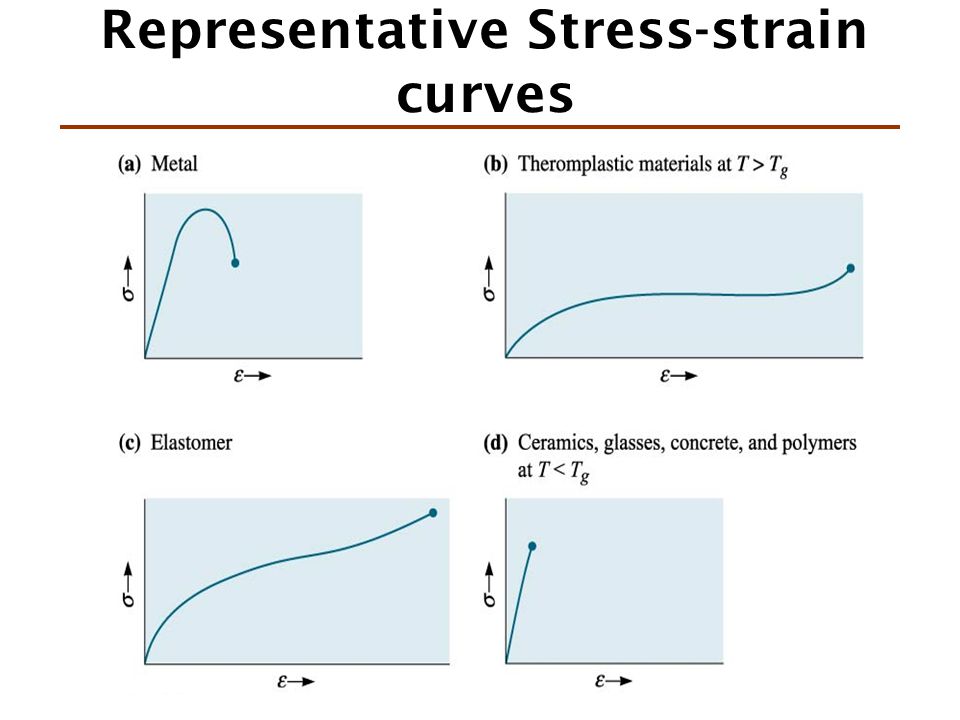
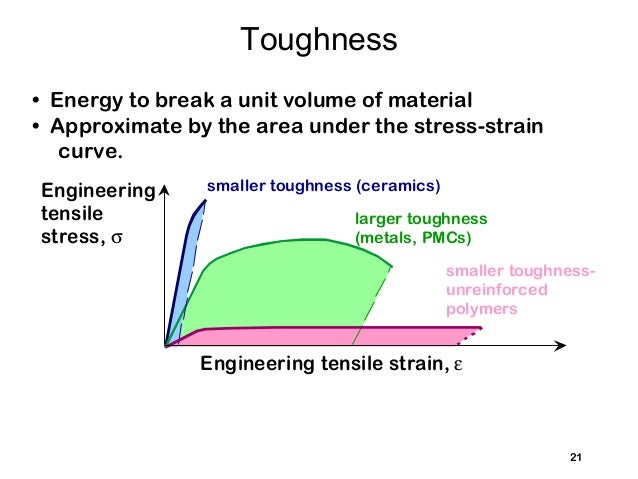
Ceramic vs metal stress strain curve.
Occurs when polymer backbones are aligned and about to break σ y engineering typical response of a metal ts stress engineering strain.
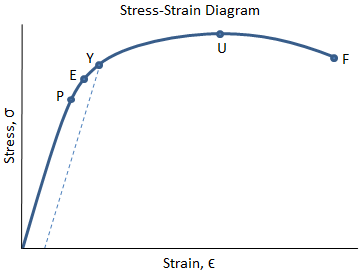
The stress at the maximum on the engineering stress strain curve metals.
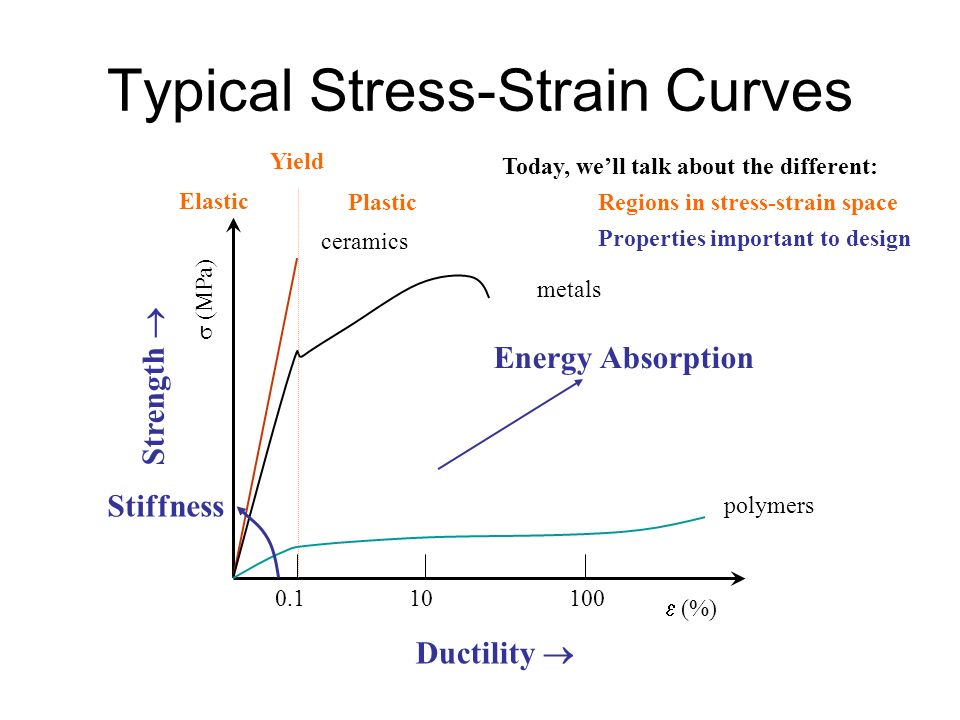
The general shape of the engineering stress strain curve fig.
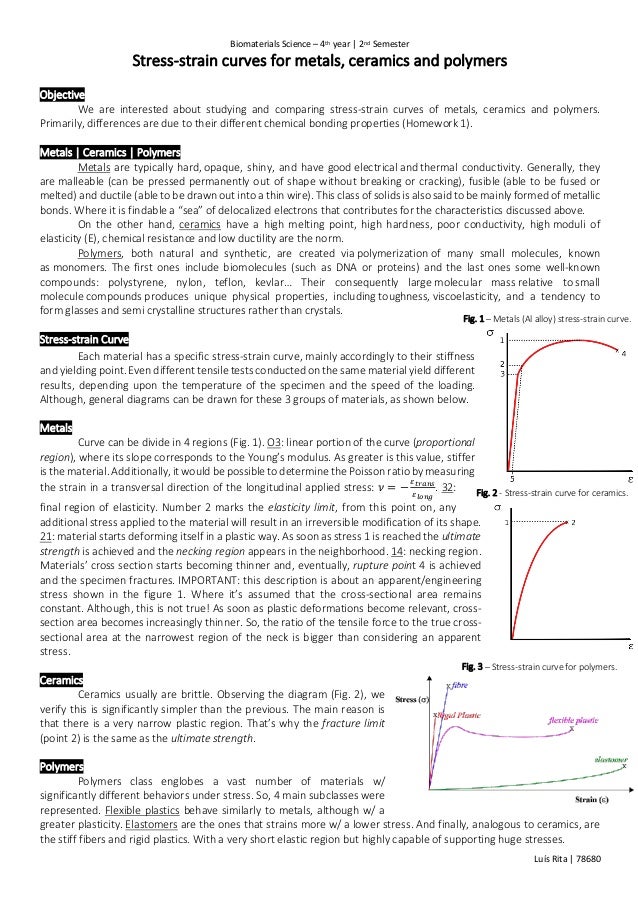
With a very short elastic region but highly capable of supporting huge stresses.
Represents straightening of the crimped ligament fibrils.
And finally analogous to ceramics are the stiff fibers and rigid plastics.
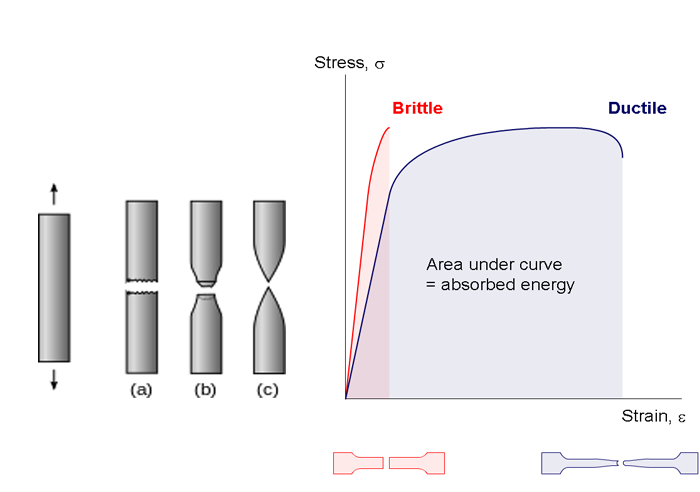
Occurs when noticeable necking starts ceramics.
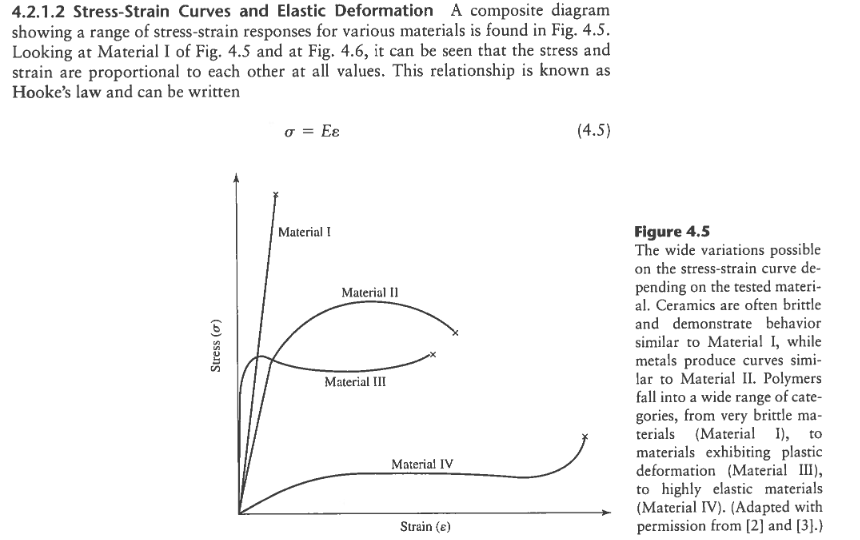
The engineering stress strain curve does not give a true indication of the deformation characteristics of a metal because it is based entirely on the original dimensions of the specimen and these dimensions change continuously during the testing used to generate the data.
The first two are strength parameters.
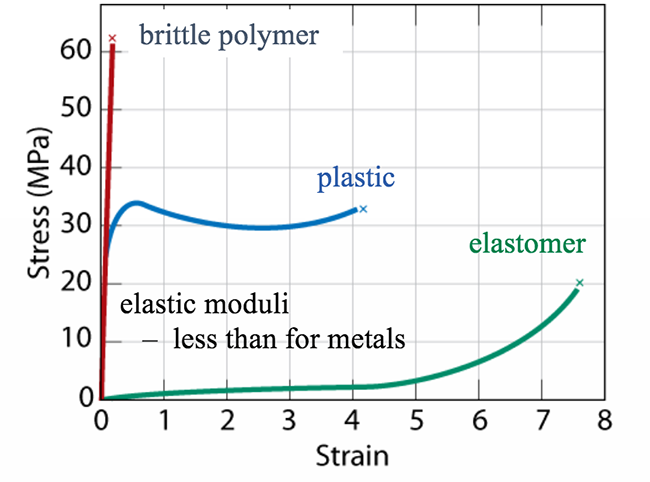
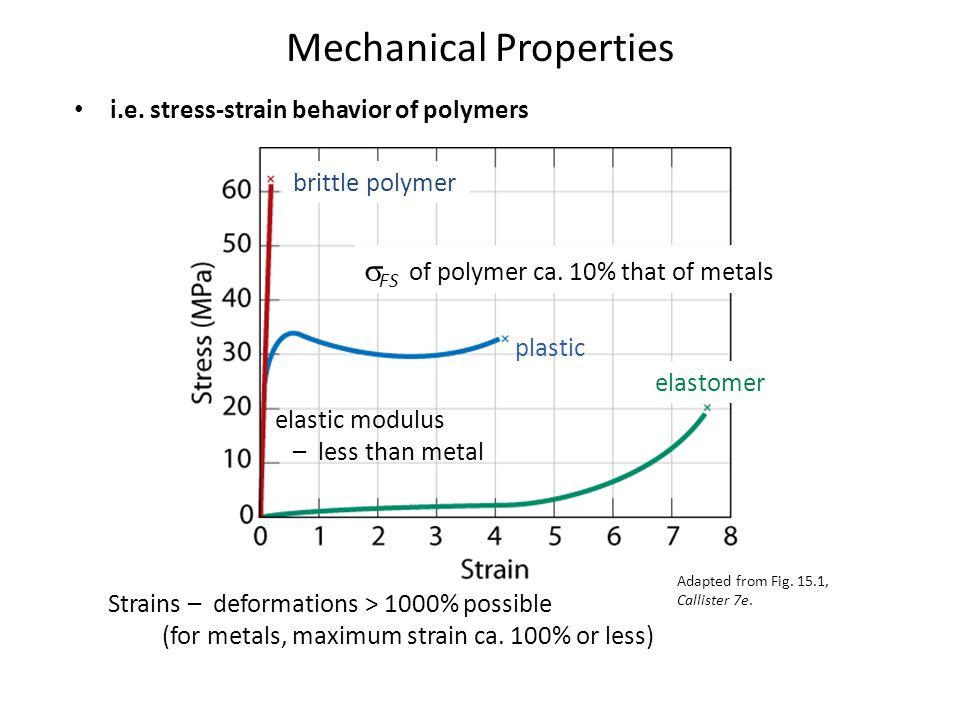
Elastomers are the ones that strains more w a lower stress.
In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain it is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing these curves reveal many of the properties of a material such as the young s modulus the yield strength.
Stress vs strain curve.
The last two indicate ductility.
Occurs when crack propagation starts polymers.
1 requires further explanation.
2 stress strain curve for ceramics.